Health & Wellness
Bariatric Surgery Treatments: Understanding Your Options
Apr 25, 2025

When choosing to have bariatric surgery, patients will have two or more surgical options to choose from, each with their own risks and benefits. The two main procedures our team performs are the roux-en-Y gastric bypass and the vertical sleeve gastrectomy. Our Bariatric team will provide guidance on what surgery would be best suited for your level of weight loss, related health challenges, and factors such as age, weight loss goals, and the ability to adapt and commit to the required lifestyle and dietary changes. Our Bariatric Surgery team will explain all of your options in detail, answer your questions and help you determine your best course of action. In the meantime, we’ve developed this blog to help you begin the learning process.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
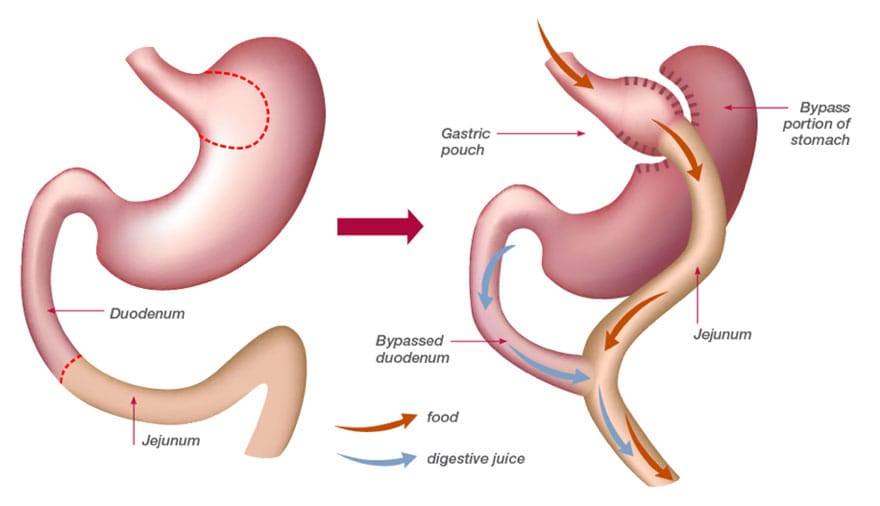
The gastric bypass surgical technique is a frequently performed bariatric surgery procedure and is the ‘gold standard’ for optimal weight loss and health. This technique assists with weight loss in two ways: it reduces the size of your stomach to limit food intake, changing the release of hormones to decrease appetite, while bypassing a portion of your small intestine to decrease the absorption of calories.
The procedure
During the procedure, a pouch is surgically attached to the middle of the small intestine (jejunum), bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine (duodenum). The pouch creates a smaller space for food intake, which helps patients feel full more quickly and decreases appetite. Bypassing part of the intestine also limits calorie absorption.
Advantages
- Limits the amount of food that can be eaten during a meal, thereby reducing the desire to eat and limiting calorie absorption.
- Produces positive metabolic changes in many organs.
- Average excess weight loss is generally higher than with gastric banding or sleeve gastrectomy.
- Clinical studies reported an average excess weight loss of 62% in 4,204 patients.
- Shown to help resolve type 2 diabetes (68%), high blood pressure (66%), obstructive sleep apnea (76%), and improve high cholesterol (95%).
- In a study of 608 gastric bypass patients, 553 of whom remained in contact, significant weight loss was still observed at 14 years out from surgery.
Risks
- Because the duodenum is bypassed, limited absorption of iron and calcium can result in iron deficiency anemia, bone calcium loss and metabolic bone disease in some patients. Deficiencies, however, can be managed through proper diet and vitamin supplements.
- Chronic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency can occur. This can usually be managed with vitamin B12 pills or injections.
- A condition known as dumping syndrome can occur when the smaller stomach pouch rapidly empties contents into the small intestine. This can be triggered when too much sugar or fat is consumed. Symptoms can include nausea, weakness, sweating, faintness and diarrhea.
- The effectiveness of the procedure may be reduced if the stomach pouch is stretched due to chronic overeating. While the procedure helps reduce appetite, patients are required to maintain a healthy, balanced diet in years following surgery in order to ensure the weight is not regained.
- Pancreatic and other digestive juices beyond the stomach can cause intestinal irritation and ulcers if patients smoke or take NSAIDs.
- The lower stomach pouch and segments of the small intestine cannot be easily seen using x-ray or endoscopy if problems such as ulcers, bleeding or malignancy should occur.
- This procedure is partially reversible as the remainder of the stomach is not removed.
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy
Like the gastric bypass, the vertical sleeve gastrectomy is a procedure that reduces the size of your stomach, resulting in a feeling of fullness after eating a smaller amount of food. It also significantly decreases the level of the powerful hunger hormone (ghrelin). However, the procedure differs in how the stomach is reduced in size and no intestinal surgery or bypassing is done.
The procedure
With the vertical sleeve gastrectomy, the surgeon creates a small stomach “sleeve” using a stapling device. This sleeve will typically hold 50 mL to 150 mL of food and is about the size of a banana. The rest of the stomach is then removed.

Advantages
- Limits the amount of food that can be eaten during a meal, thereby reducing appetite and food intake.
- Establishes a new, lower body fat set point.
- Food passes normally through the digestive tract, allowing for more absorption of vitamins and minerals. This decreases the risk of some nutrient deficiencies.
- In clinical studies, patients lost an average of 66% of their excess weight.
- The procedure is shown to help resolve high blood pressure (49%), obstructive sleep apnea (60%), and to help improve type 2 diabetes (45%) and high cholesterol (77%).
Risks
- A staple line leak is a known complication with sleeve surgery which may lead to infection or sepsis. However, should this happen, it is treatable with surgical repair, antibiotics and close monitoring.
- Irritation along the staple line can sometimes cause ulcers.
- Occasional or chronic indigestion (dyspepsia).
- Esophageal dysmotility, a condition in which food or liquid doesn’t easily pass down the esophagus, resulting in chest pain, heartburn or difficulty swallowing.
- Some nutritional deficiencies but a lower risk of anemia and bone disease.
- The procedure is irreversible as the stomach remnant is fully removed.
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that is utilized for all the procedures we offer, including gastric bypass and vertical sleeve gastrectomy. With a laparoscopic surgery, a thin tube-like video camera and narrow surgical instruments are inserted through small incisions in the abdominal wall. The surgeon views the organs and procedure on a video monitor, which provides clear 3D visualization of the surgical site for highly precise surgery.
This approach is less invasive because it replaces the need for one long incision to open the abdomen. As a result, patients can expect less post-surgical pain, less scarring, reduced time in the hospital and hospital costs, and a faster recovery time.
Laparoscopic surgery produces the same weight loss results as open surgery as it is the same surgery, just a different approach through the abdomen. It is extremely rare to need to do an open surgery. However, not all patients are candidates for this approach. Your surgeon can help you determine if this is the right approach for you.


